Ligand K-edge
Ligand K-edge XAS is a spectroscopic technique that allows the direct study of metal-ligand bonding.[1] In a XAS experiment, electrons in ligand 1s orbitals are excited to unfilled p (principal quantum number n <= 4) and continuum states. This results in a large spectral feature known as a rising edge. Transitions at energies lower than the edge can occur, provided they are to orbitals with some ligand p character, and are called pre-edges. Such transitions are often observed in the data of complexs with metal-ligand bonding.
Pre-edge intensities (D0) are related to the amount of ligand (L) character in the unfilled orbital:
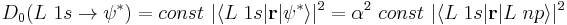
where 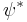 is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and
is the wavefunction of the unfilled orbital, r is the transition dipole operator, and 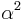 is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since
is the "covalency" or ligand character in the orbital. Since 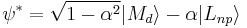 , the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values:
, the above expression relating intensity and quantum transition operators can be simplified to use experimental values:
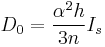
where n is the number of absorbing ligand atoms, h is the number of holes, and Is is the transition dipole integral which can be determined experimentally. Therefore, by measuring the intensity of pre-edges, it is possible to experimentally the determine the amount of ligand character in a molecular orbital.
References
- ^ Solomon, E.; Hedman, B.; Hodgson, K.; Dey, A.; Szilagyi, R. (2005). "Ligand K-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy: covalency of ligand–metal bonds". Coordination Chemistry Reviews 249: 97–76. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.03.020.